최근 새로 담당하게 된 프로젝트의 프레임워크는 순수 Spring MVC 5.2.9 버전이다.
어노테이션 방식을 사용하는 Spring Boot 프로젝트만 익숙했기에, 많은 설정이 xml파일을 통해 이뤄져있는 순수 Spring은 굉장히 낯설었다. 이에 어려움을 겪었던 부분에 대해 기록해자.
1. 빈 등록 문제
배경
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Configuration
public class JwtConfig {
...
@Bean
public JwtManager jwtManager() {
return new JwtManager(...);
} // 빈 등록 안됨
@Bean
public JwtAuthenticationFilter jwtAuthenticationFilter(JwtManager manager) {
return new JwtAuthenticationFilter(manager);
}
}JWT를 활용한 인가를 위해 필터와 관리 클래스를 빈으로 등록했고, 필터는 JWT 관리 클래스를 빈으로 주입받게 된다.
위와 같은 Java class 설정으로 애플리케이션을 실행하면 다음과 같은 예외가 발생했다.
org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No bean named 'jwtAuthenticationFilter' available
root-context.xml에 직접 빈을 등록한 경우엔 정상적으로 등록되었다.
하지만 빈 등록 자체에 문제가 없다면 Java class를 통한 빈 등록 또한 정상 동작해야 했다.
문제 원인
결론부터 말하자면 Java class로 빈을 등록할 경우, Root WebApplicationContext에 빈 자체가 등록되지 않아 DelegatingFilterProxy가 위임 빈을 내부에 저장할 때 jwtAuthenticationFilter를 찾지 못해 발생한 문제였다.
이는 root-context.xml에 아래와 같은 컴포넌트 스캔 태그가 없었기 때문이다.
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.project.*" />Spring Boot와 달리 xml 파일에 컴포넌트 스캔을 명시해줘야 Java class로 설정된 빈을 등록할 수 있었다.
원인을 찾는 과정에서 다음 두 가지에 대한 개념이 도움되었다.
- Spring Context의 로드 순서와 관계
- DelegatingFilterProxy의 동작 시점
Spring Context의 로드 순서와 관계
Spring Context는 크게 두 가지로 구분할 수 있으며 관계는 다음 그림과 같다.
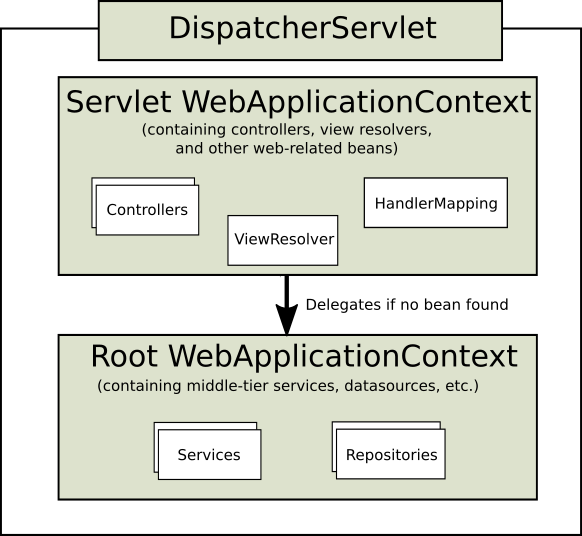
그림에서 볼 수 있듯 Servlet WebApplicationContext는 Root WebApplicationContext에 의존하게 된다.
다시 말해, Root WebApplicationContext와 Servlet WebApplicationContext는 부모-자식 관계라고 볼 수 있다.
그러므로 Servlet WebApplicationContext에선 Root WebApplicationContext의 빈을 참조할 수 있지만 그 반대는 참조할 수 없다.
두 개의 컨텍스트는 다음 그림과 같은 순서로 로드된다.
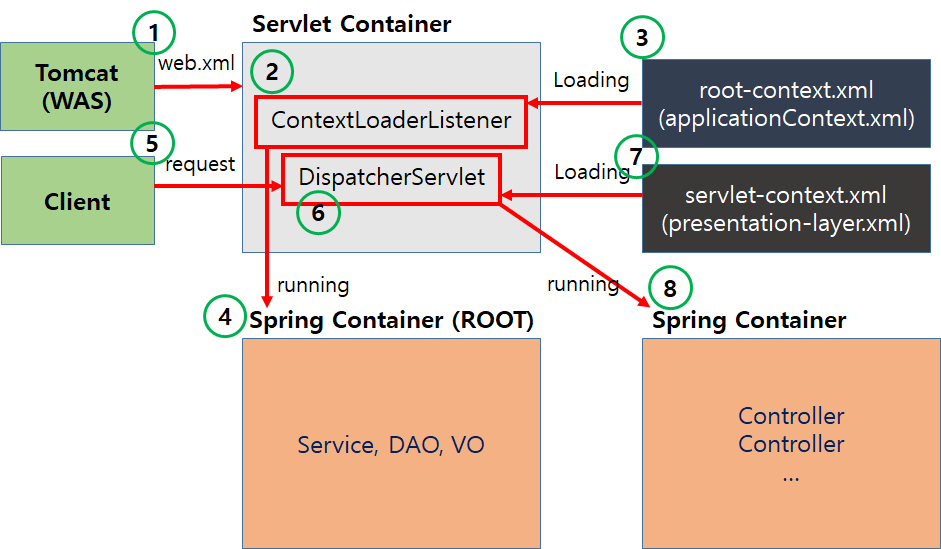
1. 톰캣은 web.xml을 읽어 프로젝트와 관련된 설정을 읽어들임
2 ~ 4. web.xml에 설정된 ContextLoaderListener를 통해 Root WebApplicationContext를 초기화
- 이 때, 설정 값으로 web.xml에 <context-param> 태그에 명시된 xml 파일을 로드한다.
- ContextLoaderListener는 부모 클래스인 ContextLoader의 initWebApplicationContext()를 호출해 초기화
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
...
try {
// 스프링 컨테이너 생성
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
...
// 서블릿 컨테이너에 스프링 컨테이너(Root Context)를 설정
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
...
}
}
5 ~ 8. ServletWebApplicationContext 초기화
- 그림 상에선 클라이언트 첫 요청이 들어오면 DispatcherServlet이 생성되고, Servlet WebApplicationContext가 생성되는 것으로 나와 있다.
- 하지만 이는 web.xml에 서블릿 초기화 태그 내부에 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 태그가 존재하지 않는 경우에만 해당한다.
- <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 태그가 존재한다면 애플리케이션 시작 시점에 초기화되며, 이 방식이 권장된다.
- ServletWebApplicationContext의 초기화는 DispatcherServlet의 부모 클래스인 FrameworkServlet이 initWebApplicationContext()를 호출해 초기화한다
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 앞서 Servlet Context에 초기화된 Root Context를 가져옴
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 현재 서블릿에 Spring Context가 존재한다면 수행(마찬가지로 Root Context를 부모로 설정)
// 생성자를 통해 주입된 컨텍스트인 경우
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
...
}
// Servelt Context에 등록된 Spring Context가 존재한다면 등록
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
// 모든 경우 없다면 새로 생성
if (wac == null) {
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
...
// DispatcherServlet에 Servlet WebApplicationContext 저장
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
...
// 파라미터로 받은 Root Context를 부모로 설정
wac.setParent(parent);
...
return wac;
}
여기서 가장 중요한 점은 Root WebApplicationContext가 Servlet WebApplicationContext보다 먼저 생성되며, 부모 Context로 초기화된다는 것이다.
** Spring Context와 Servlet Context **
Root WebApplicationContext, Servlet WebApplicationContext 모두 Spirng Context라고 할 수 있다.
이름이 Servlet WebApplicationContext라고 Servlet Context인 것은 아니며, Spring Context는 단지 Servlet Context 위에서 동작하는 것 뿐이다.
다만, Root WebApplicationContext는 Servlet Context의 속성으로 직접적으로 등록되는 것이고,
ServletWebApplicationContext는 특정 서블릿(DispatcherServlet)에 종속되며, 이 Servlet을 통해 Servlet Context에 등록 되는 것이다.
DelegatingFilterProxy의 동작 시점
DelegatingFilterProxy의 존재 이유와 작동 방식은 Spring docs를 확인하자.
DelegatingFilterProxy가 Servlet Context의 필터 체인에 등록되는 시점은 톰캣이 web.xml 또는 @WebServlet을 통해 설정을 읽어들일 때다.
이후 Root WebApplicationContext가 초기화 되고, DelegatingFilterProxy에 실제로 위임할 빈이 내부에 저장된다.
이 때, DelegatingFilterProxy가 빈을 찾기 위해 접근하는 Context가 바로 Root WebApplicationContext다.
@Override
protected void initFilterBean() throws ServletException {
synchronized (this.delegateMonitor) {
if (this.delegate == null) {
if (this.targetBeanName == null) {
this.targetBeanName = getFilterName();
}
WebApplicationContext wac = findWebApplicationContext();
if (wac != null) {
this.delegate = initDelegate(wac);
}
}
}
}
/**
* findWebApplicationContext() 메서드를 따라가다보면 Root Context를 찾는 것을 알 수 있다.
**/
@Nullable
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(sc, WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
** DelegatingFilterProxy는 Spring Security 의존성을 추가해야만 사용할 수 있다? **
아니다. 아래에서 볼 수 있듯 DelegatingFilterProxy는 Spring Framework 자체에 포함되어 있다.
package org.springframework.web.filter;
...
public class DelegatingFilterProxy extends GenericFilterBean {
...
}결론
- Spring Context는 크게 두 가지로 구분할 수 있다.(Root WAC, Servlet WAC)
- 각 Context는 일반적으로 root-context.xml, servlet-context.xml 파일에서 설정 값을 로드한다.
- Root WAC와 Servlet WAC는 부모-자식 관계와 같으며, 1:N 관계를 가진다.
- DelegatingFilterProxy가 필터 체인에 등록되는 시점은 톰캣이 web.xml을 통해 설정을 로드할 때다.
- DelegatingFilterProxy가 위임할 빈을 저장하는 시점은 Root WAC 초기화 이후이다.
- root-context.xml에서 컴포넌트 스캔을 하지 않아 Root WAC에 해당 빈이 등록될 수 없었다.
- Servlet WAC에만 필터가 등록된다면 기본적으로 DelegatingFilterProxy는 위임할 빈(필터)을 찾을 수 없다.
해결 방안
앞선 원인 분석 과정을 거치며, jwtAuthenticationFilter 빈이 Servlet WebApplicaitonContext에만 존재하고, Root WebApplicationContext엔 존재하지 않음을 확인했다. 이는 servlet-context.xml에만 컴포넌트 스캔 태그가 존재했고, root-context.xml엔 존재하지 않았기 때문이다.
해결을 위해 root-context.xml에 컴포넌트 스캔 태그를 추가했다.
이 과정에서 Root WebApplicationContext, Servlet WebApplicationContext에 빈이 이중으로 등록되며 같은 메서드가 두 번 호출되는 이슈가 발생했는데 servlet-context.xml의 스캔 범위를 조절하여 해결했다.
2. 환경 설정 파일 인식
앞선 빈 등록 문제와 함께 application.properties, yml과 같은 환경 설정 파일에 설정된 값이 @Value를 통해 변수에 주입되지 않는 문제가 존재했다.
이 문제도 마찬가지로 root-context.xml에 아래와 같은 환경 설정 파일 빈 등록 태그가 없었기 때문에 발생했던 문제였다.
<bean id="properties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
// Spring 3.1부터 권장되는 방식
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.context.support.PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer">
3. 선언적 트랜잭션 관리, AOP 프록시 방식의 차이
개발 단계에서 테스트 중, unchecked exception이 발생해도 롤백이 되지 않는 현상을 발견했다.
Spring Boot에선 @Transactional만 붙이면 CGLIB를 사용해 선언적 트랜잭션 방식을 사용할 수 있었다.
원인을 찾다보니 내가 진행 중인 프로젝트에 아래와 같은 태그가 xml 파일에 존재하지 않아 생겼던 문제였다.
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true"/>이 태그를 설정하니 손쉽게 해결했고, 태그의 역할에 대해 알아보자.
<tx:annotation-driven>
이 태그는 @Transactional을 사용하여 선언적 트랜잭션 관리를 하겠다는 의미이다.
즉, @Transactional이 정상 작동하려면 이 태그가 존재해야 한다.
transaction-manager="transactionManager"
이 속성은 말 그대로 TransactionManager를 설정하는 속성이다.
여기에 등록된 TrasnactionManager가 기본 값으로 사용된다.
다중 DB 커넥션이 필요한 경우 별도로 TransactionManager를 생성하게 되는데, 이 경우 @Transactional의 value 설정에 해당 TransactionManager의 이름을 등록해주면된다.
proxy-target-class="true"
동적 프록시 생성 방식을 결정하는 속성이다.
기본 값은 false로 JDK 동적 프록시를 사용하게 된다. true일 경우 CGLIB를 사용하게 된다.
두 프록시 생성 방식의 차이는 구체 클래스를 통해 프록시를 생성할 수 있냐 아니냐에 있다.
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring - @Transactional 활용해 멀티 스레드 환경을 테스트할 때 주의점 (0) | 2024.05.06 |
|---|---|
| Spring - 요청 파라미터 LocalDate타입 필드에 바인딩 및 검증 (1) | 2024.04.12 |
| Spring - Springboot + Vue3 + MariaDB를 카페24에 배포할 때 Tip(주의사항) (1) | 2023.07.26 |
| Spring - ArgumentResolver (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| Spring - DispatcherServlet에 대해 알아보자 (0) | 2023.07.15 |
